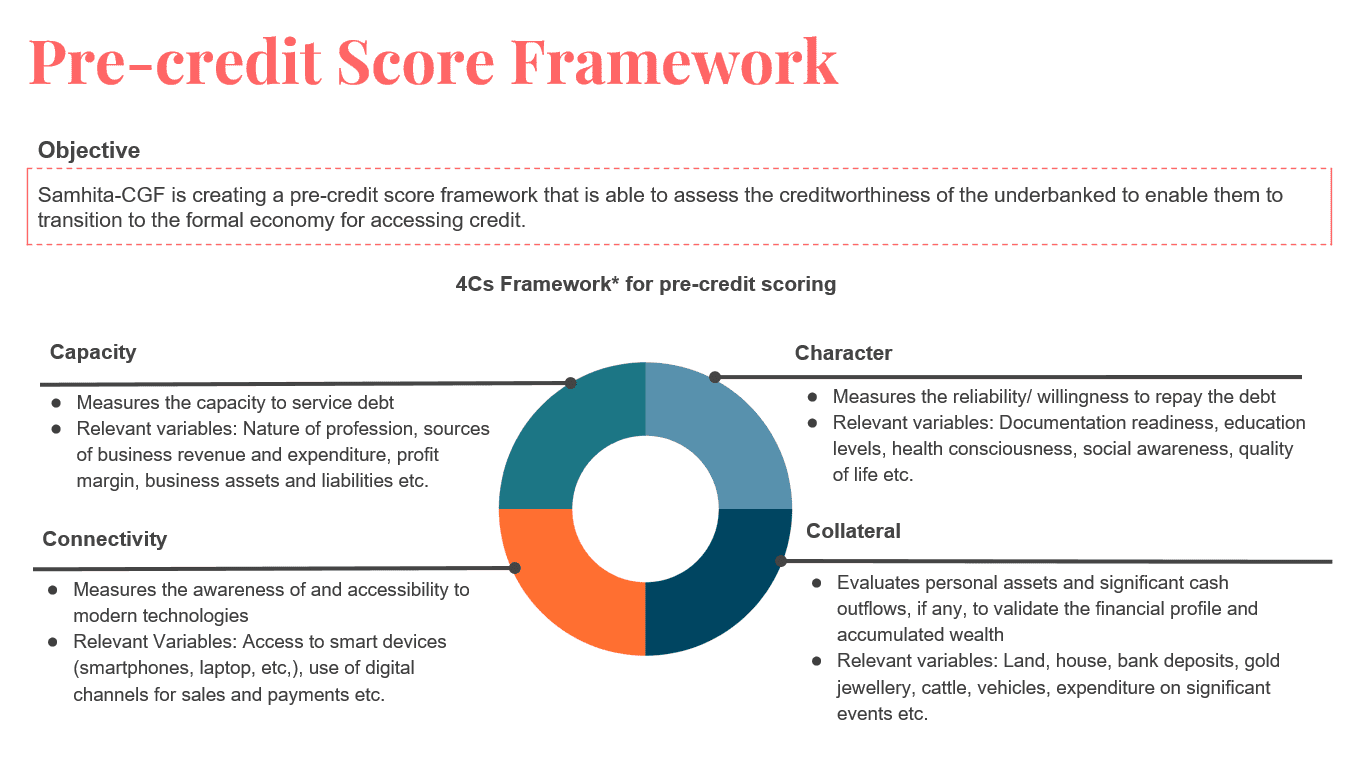
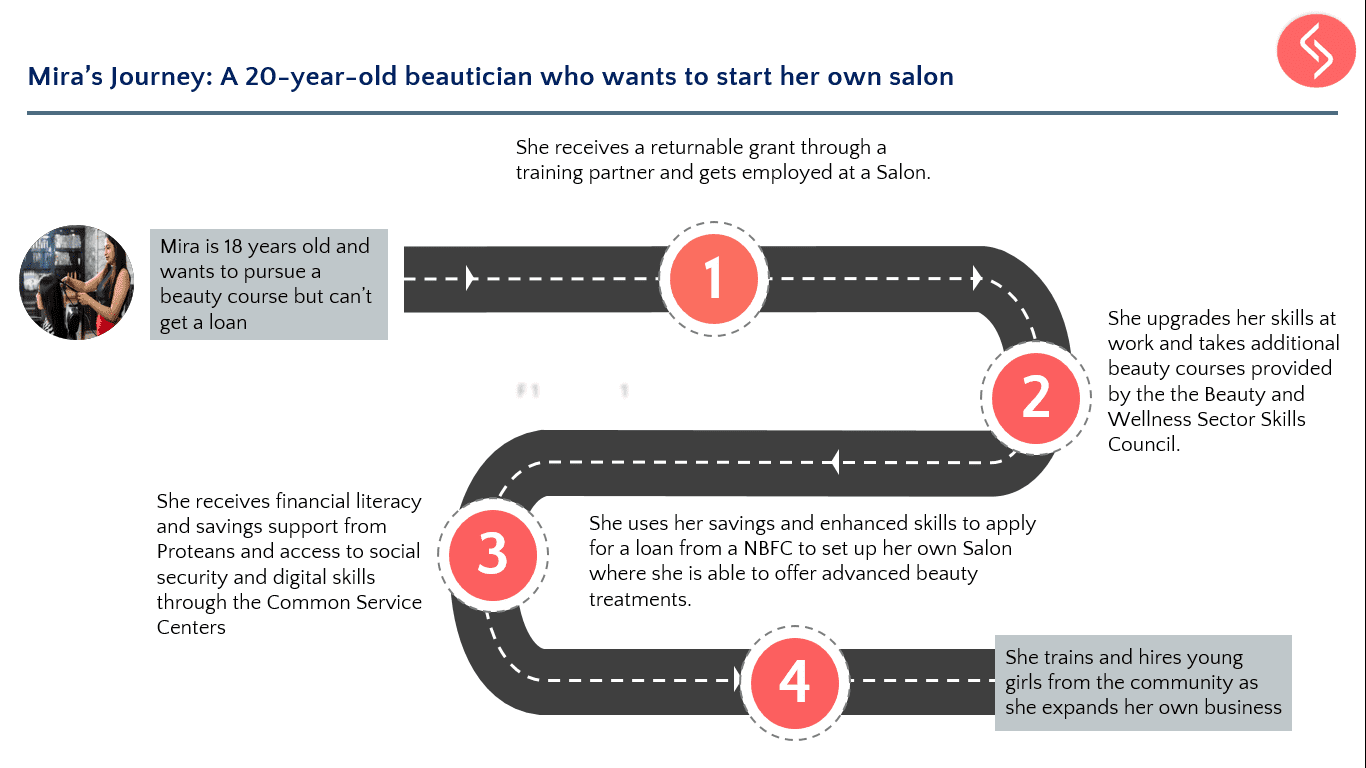
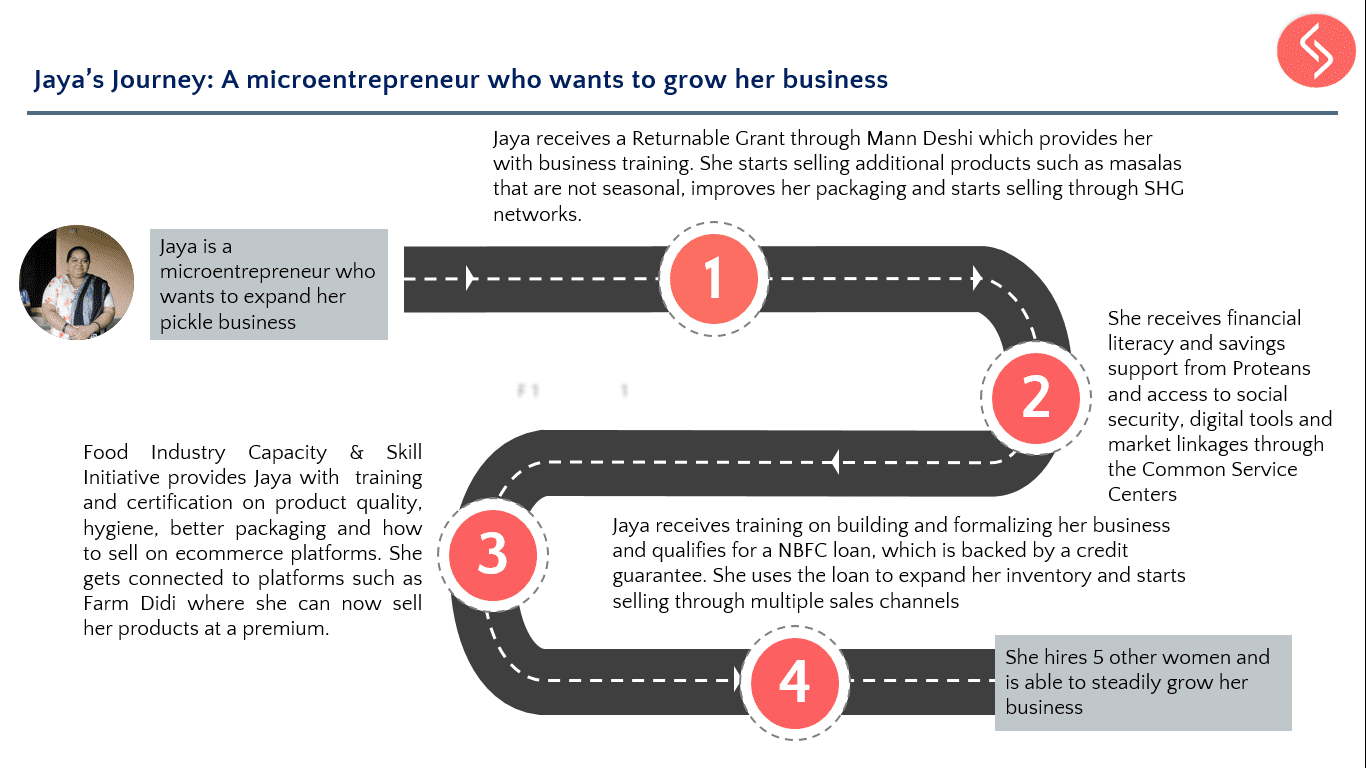
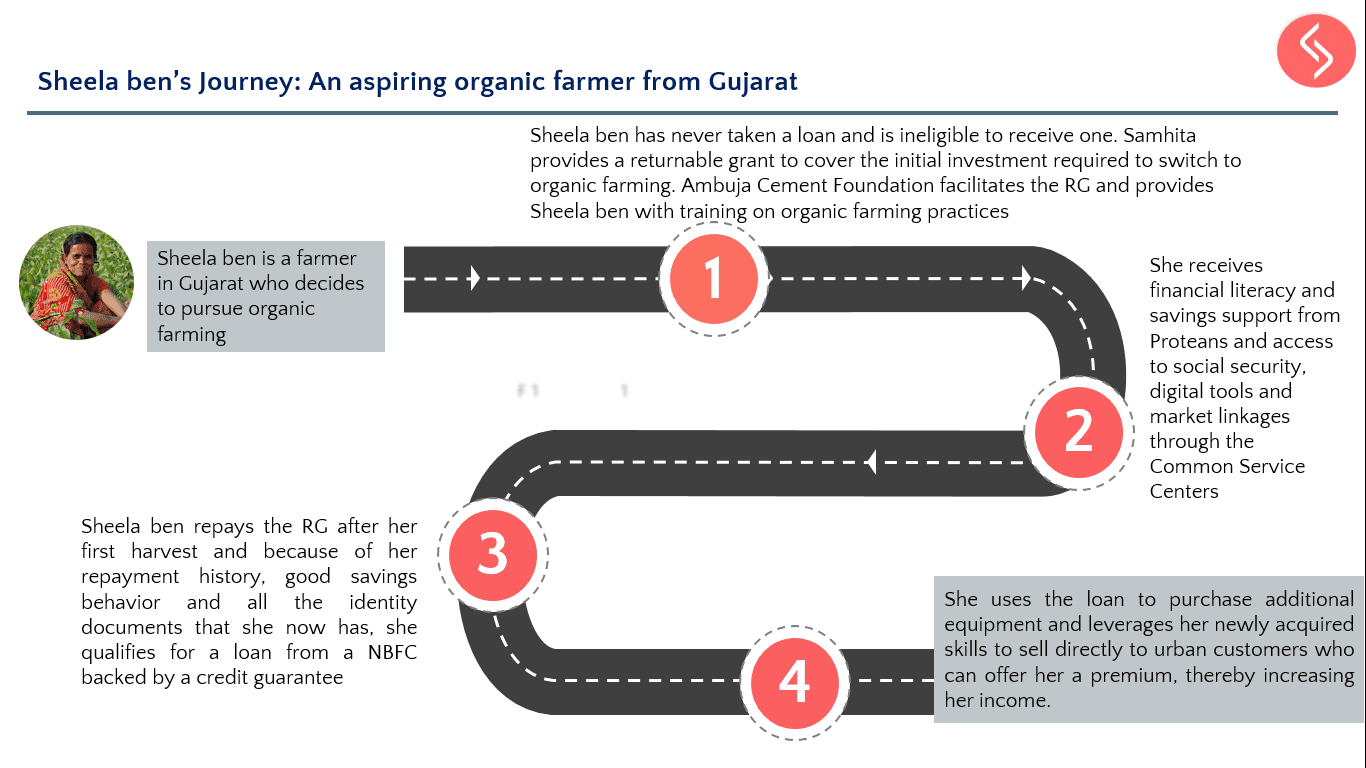
As part of its CSR services, Samhita Social Ventures undertakes community needs assessment for companies to align the expectations and intentions of the company with priorities identified by the community that it seeks to benefit as a key stakeholder. This is accomplished by conducting door-to-door surveys, interviews with key informants in the village (such as sarpanch, asha worker, aanganwadi workers) and focused group discussions with the residents.
Through our intense and in-depth interaction with communities across the country, we have realized that community participation and acceptance are critical in ensuring the success of CSR programs. While the theoretical discourse on development has always acknowledged the importance of participatory approach (you may have heard of Robert Chambers and Paulo Freier), this takes on a pragmatic connotation for companies beginning to think about CSR in India.
Our work has shown that the aim should be to address social implications of corporate activities by securing community participation in decision-making and consideration of local knowledge and the environment. The community should drive and own these initiatives. Any tendency to superimpose or force CSR or other development initiatives top-down on communities could be disastrous.
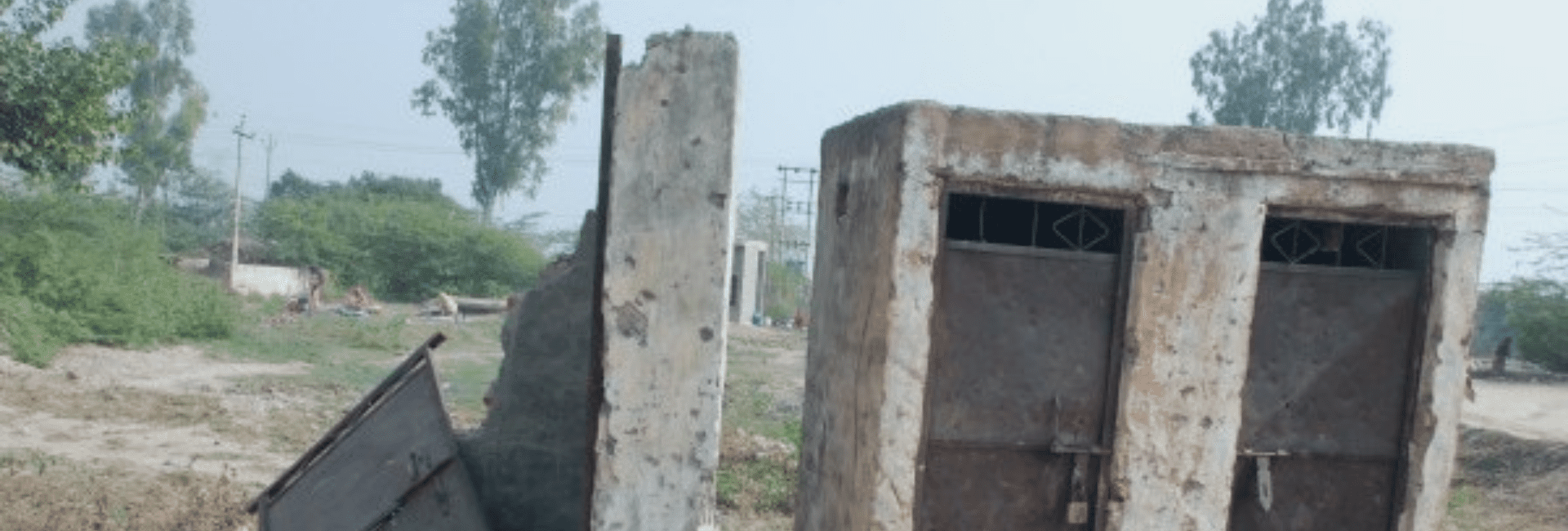
So for example, during one such assessment in two clusters of Vadodara District, Gujarat it was observed that 87% people defecate openly every day. While reducing open defecation is a national and international priority, it was most interesting to note that communities in one cluster did not perceive it to be an issue. The assessment found that these communities defecated in the open not only because of the unavailability of toilets but due to low awareness of the potential health hazards, internalized behavior, accustomed practice, perception of high costs of maintaining and constructing toilets, caste based differences in terms of maintenance and cleaning, etc. It was seen that these communities appeared resistant to using toilets because of all these reasons. In this context, CSR initiatives of companies to set-up toilets for such communities to eliminate open defecation, disregarding the voices of the community, would be futile and bound to fail. The company would have, in effect, spent its funds putting up concrete structures with its branding – not used by anyone and soon falling into a state of disrepair and neglect. In fact, this is a very common sight in many villages dotted across India. One of the ways to then incorporate the community’s views and mitigate the risk of failure would be to start a behavior change communication or campaign on a long term and sustained basis. Another example flows from the needs assessment conducted in northern India. The study revealed rampant usage of traditional fuel for cooking. About 83% of people relied on cow-dung and wood as the means of cooking. It was obvious to our eyes that this was leading to many respiratory problems among women and also causing indoor pollution. Surprisingly, the women did not seem to be too bothered. When we suggested using smokeless chullahs or stoves, most of them thought it to be flippant. Conversations with these women revealed that they preferred these smoke generating stoves because they believed that it kept the house warm, drove away insects etc. They said that they were accustomed to cooking in this way. It is anyone’s guess as to what the results of a CSR initiative distributing free smokeless stoves to a community like this would be. Promoting smokeless chulhas in such households becomes challenging unless their beliefs are changed.
A similar reaction was observed in another needs assessment study when a group of women said they did not want personal taps and that they preferred community pumps as it was the only activity that gave them a chance to come out of their houses and socialize with other women.
In conclusion, we opine that CSR initiatives by companies or social developmental activities by NGOs should be planned in a participatory manner, in consultation with the community, literally sitting with them, and gauging their basic needs. We must take recourse to “participatory rural appraisal” and other mapping tools to identify the community needs. This, in turn, results in greater outreach and smoother implementation. And thus, a project is born.